Polling Example
This example shows how to receive bot messages using polling instead of webhooks. The pattern shown here can be adapted, for example by polling in your frontend.
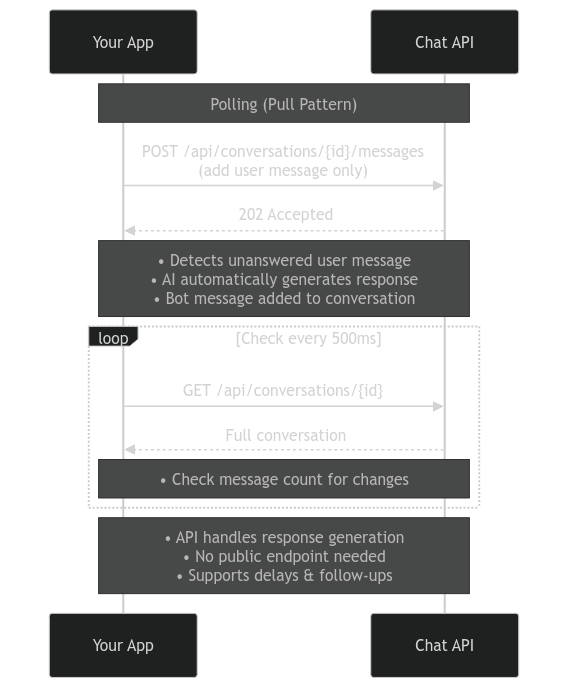
How It Works
Core API Pattern:
- Create a bot and conversation
- Poll
GET /api/conversations/{id}at regular intervals - When new messages arrive, update your UI
- Send user messages via
POST /api/conversations/{id}/messages
Step 1: Set Up Imports and Configuration
import requests
import time
import threading
import os
API_KEY = "sk_yourapikey"
BASE_URL = "https://api.prioros.com/v3"
headers = {
"Authorization": f"Bearer {API_KEY}",
"Content-Type": "application/json"
}
print("Setting up chat...\n")
Step 2: Create a Bot
Create a bot with a personality and attributes:
bot_response = requests.post(
f"{BASE_URL}/api/bots",
headers=headers,
json={
"name": "Anna",
"freeform": "You're energetic and passionate",
"attributes": [
{"name": "bio", "value": "Certified personal trainer specializing in HIIT"},
{"name": "age", "value": "28"},
{"name": "location", "value": "Miami, FL"}
]
}
)
bot = bot_response.json()['bot']
bot_id = bot['id']
print(f"✓ Bot created")
print(f" ID: {bot_id}")
print(f" Name: {bot['name']}")
print(f" Attributes: {bot['attributes']}\n")
Step 3: Create a Conversation
Create a conversation between the bot and a user:
conversation_params = {
"bot_id": bot_id,
"user_id": "user_sarah_m",
"create_user_if_not_exists": True
}
conversation_response = requests.post(
f"{BASE_URL}/api/conversations",
headers=headers,
json=conversation_params
)
conversation = conversation_response.json()['conversation']
conversation_id = conversation['id']
print(f"✓ Conversation created")
print(f" ID: {conversation_id}")
print("=" * 60)
print("Press Ctrl-C to exit")
print("=" * 60 + "\n")
Step 4: Poll for Messages
Set up a function to poll for new messages at regular intervals:
def poll_for_messages():
"""Polls for new messages"""
last_displayed = 0
while True:
# Get conversation
response = requests.get(
f"{BASE_URL}/api/conversations/{conversation_id}",
headers=headers
)
conversation = response.json()
messages = conversation['messages']
# Update display if new messages arrived
if len(messages) != last_displayed:
display_conversation(messages)
last_displayed = len(messages)
time.sleep(0.5) # Poll every half second
Step 5: Send Message Function
Create a function to send user messages:
def send_message(text):
"""Send a user message to the conversation"""
response = requests.post(
f"{BASE_URL}/api/conversations/{conversation_id}/messages",
headers=headers,
json={
"message": {
"text": text,
"from_bot": False
}
}
)
response.raise_for_status()
Step 6: Display Functions (Terminal UI)
These functions handle the terminal display. This is just for showing messages and is not relevant to the Priori Labs API:
def clear_screen():
"""Clear the terminal screen"""
os.system('cls' if os.name == 'nt' else 'clear')
def display_conversation(messages):
"""Clear screen and display all messages"""
clear_screen()
print("Chat with AI Bot (takes 10-15 seconds to respond)")
print("=" * 60)
for msg in messages:
sender = "🤖 Bot" if msg['from_bot'] else "👤 You"
print(f"\n{sender}: {msg['text']}")
print("\n" + "=" * 60)
print("> ", end='', flush=True)
Step 7: Interactive Chat Loop
Start the polling thread and run the interactive chat loop:
# Start polling in background
polling_thread = threading.Thread(target=poll_for_messages, daemon=True)
polling_thread.start()
# Interactive chat loop
try:
while True:
user_input = input("Your message: ")
if user_input.strip():
send_message(user_input)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
exit(0)
What's Happening Behind the Scenes?
When you poll for messages:
- Your app requests the full conversation every 500ms
- The API returns all messages in the conversation
- You compare the message count to detect new messages
- When new messages arrive, you update your UI
- The bot generates responses automatically when it detects unanswered user messages
This pattern gives you control over when to check for updates, without requiring a publicly accessible endpoint like webhooks do.
Key API Patterns
Creating Resources:
POST /api/bots- Create a bot with personality and attributesPOST /api/conversations- Create a conversation, link a user and bot together
Receiving Messages:
GET /api/conversations/{id}- Returns full conversation including all messages- Poll this endpoint at intervals (500ms shown here)
Sending Messages:
POST /api/conversations/{id}/messages- Send a message in the conversation- Set
from_bot: falsefor user messages
Adapting for Frontend
This pattern translates directly to frontend applications:
- Use
setInterval()or similar to poll the conversation endpoint - Update your UI state when new messages arrive
- Send user messages on form submission or button click
Next Steps
Receiving Messages OverviewCompare webhooks, polling, and generate-response patterns
Webhooks ExampleRecommended pattern for automatic real-time message delivery
Generate Response ExampleSynchronous pattern for human-in-the-loop workflows
Production Tips
For production use:
- Adjust polling interval based on your needs (500ms is aggressive, 2-5 seconds is often sufficient)
- Implement exponential backoff if API errors occur
- Consider using webhooks instead for more efficient real-time updates
- Add error handling for network failures